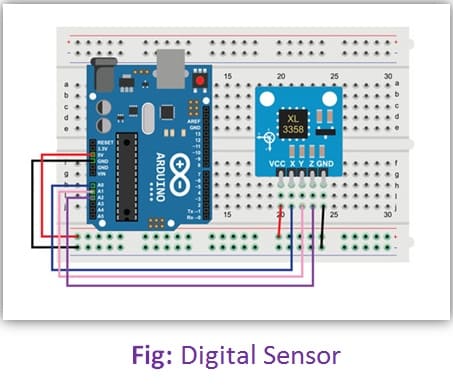
Analog Sensors:
Analog sensors produce a continuous output signal or voltage which is generally proportional to the quantity being measured. Physical quantities such as Temperature, Speed, Pressure, Displacement, Strain, etc are all Analog quantities as they tend to be continuous in nature. For example, the temperature of a liquid can be measured using a thermometer which continuously responds to temperature changes as the liquid is heated up or cooled down.
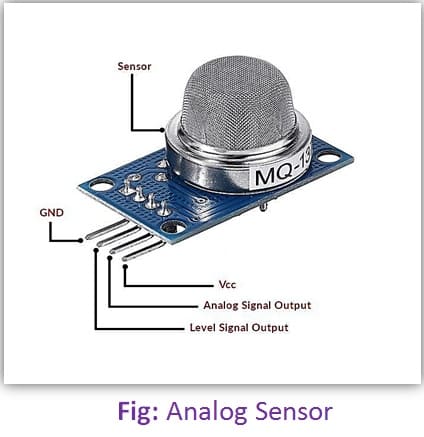
Digital Sensors:
As its name implies, Digital sensors produce a discrete digital output signals or voltages that are a digital representation of the quantity being measured. Digital sensors produce a Binary output signal in the form of a logic “1” or a logic “0” (“ON” or “OFF”). This means that a digital signal only produces discrete values which may be outputted as a single bit or by combining the bits to produce a single “byte” output.