Pi Bond:
A pi (π) bond is formed by side-wise overlapping of p-orbitals. The electrons that occupy a π-bond are called π-electrons. Now, since the sidewise overlapping is only partial, the bonds formed are weak bonds, and π-electrons are more loosely held than σ-electrons and are of higher energy. As a result, π-bonds are more easily broken and are more reactive than σ-bonds. So, C2H4 is much more reactive than methane.
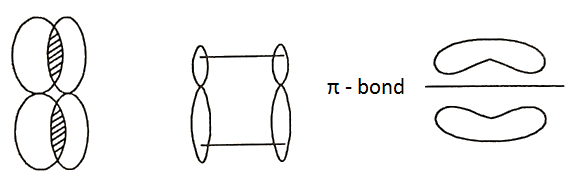
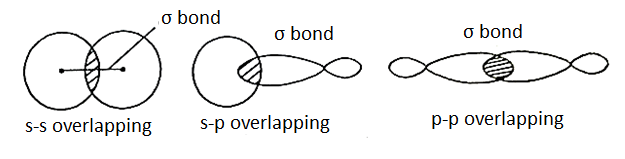
Sigma Bond:
A bond formed by end-to-end overlapping of s-s, s-p, or p-p orbitals is called σ-bond. Now, since the orbitals overlap along their axis, maximum overlapping is possible and hence the σ-bond formed is strong. Electrons that occupy a σ-bond are called σ-electrons.