Different Types of Robots:
There are six main types of industrial robots:
1. Cartesian:
The most commonly used robots type for the majority of industrial applications is Cartesian. Plant operators often default to this type because they are easy to use and program. The linear movements of the Cartesian elements give the robot a cube-shaped workspace that fits best with pick and place applications. It can range from 100 millimeters to tens of meters. These robots are also a popular choicer because they are highly customizable.

Customers can determine the stroke lengths, speed and precision of the robots because most of the parts arrive separately and assembled by the machine builders. That being said, one drawback to Cartesian robots is the complexity of assembly required. Overall, plant operators choose this robot design most often for the flexibility in their configuration that allows them to meet specific application needs.
2. Cylindrical:
Cylindrical robots are very simple and similar to Cartesian in their axis of motion. Most Cylindrical robots are made of two moving elements rotary and linear actuators. Because they have a cylindrical work envelope, machine designers might select them for their economy of space.

The robot can be placed in the middle of a workspace and because of its rotation element, it can work anywhere around it. Simple applications where materials are picked up, rotated and then placed work best for Cylindrical robots. Installation and use are not complex, and they come as fairly complete solutions with minimal assembly.
3. Polar:
Polar robots also called spherical robots. In this configuration, the arm is connected to the base with a twisting joint and a combination of two rotary joints and one linear joint. The axes form a polar coordinate system and create a spherical-shaped work envelope.

4. SCARA:
SCARA robots often a more complete solution then the Cartesian or Cylindrical. They are all-in-one robots, meaning a SCARA robot is equipped with x, y, z and rotary motion in one package that comes ready-to-go, apart from the end-of-arm tooling. The work envelope is similar to Cylindrical robots but it has more degrees of motion in a radius or arch-shaped space.

SCARA robots can move quicker than Cartesian or Cylindrical robots. They are seen often in bio-med applications due to to their small work area. SCARA robots commonly used in assembly applications, this selectively compliant arm for robotic assembly is primarily cylindrical in design. It features two parallel joints that provide compliance in one selected plane.
5. 6-Axis:
Another all-in-one robot type is the 6-axis. Though sometimes 6-axis robots can be almost toy-sized, they are typically very large and used for large assembly jobs such as putting seats into a car on an assembly line. These robots operate like a human arm and can pick up materials and move them from one plane to another.
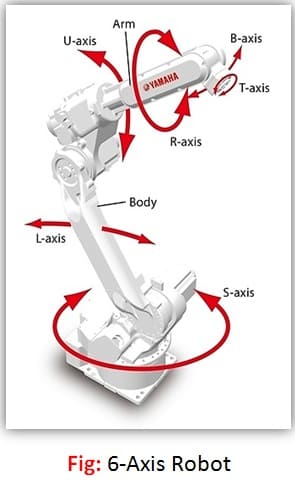
6-axis robots can move quick and come in complete solutions like SCARAs, however their programming is more complicated. The robots can get so large and move so quickly that if roller coaster seats were attached to them. They could simulate an amusement park ride.
6. Delta:
Delta robots are the fastest and most expensive. They have a unique, dome-shaped work envelope in which they can achieve very speeds. Delta robots are best for fast pick-and-place or product transfer applications like moving parts from a conveyor belt and placing them in boxes or onto another conveyor belt. They also come as complete solutions for machine designers. The main advantage of delta robots is their speed and precision with which they operate.
